In architectural engineering, the right software is not just a tool, but a partner in design. This article dives into the best architectural engineering software, highlighting tools that have become indispensable for architects. From the precision of AutoCAD to the intuitive BIM capabilities of Revit, each program offers unique strengths that cater to various facets of architectural creativity.
Whether it’s 3D modelling in SketchUp or detailed construction documentation in ArchiCAD, these tools are the backbone of modern architectural design. We will explore how each software shapes the way architects bring their visionary structures to life, balancing functionality, efficiency, and aesthetic appeal. Join us in uncovering the software that is not just about creating buildings, but about envisioning the future of architectural design.
Top 11 Architectural Engineering Software
Here’s a table containing architectural engineering software with their name, parent company, and why architects use them:
| Rank | Software Name | Parent Company | Usage by Architects |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AutoCAD | Autodesk | Widely used for 2D and 3D CAD design |
| 2 | Revit | Autodesk | Popular for building information modeling (BIM) |
| 3 | SketchUp | Trimble | Known for its user-friendly interface for 3D modeling |
| 4 | ArchiCAD | Graphisoft | A BIM software popular among architects |
| 5 | Rhino 3D | Robert McNeel & Associates | Used for complex 3D modeling, particularly in architecture and industrial design |
| 6 | 3ds Max | Autodesk | Renowned for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering |
| 7 | Civil 3D | Autodesk | A civil engineering design and documentation software |
| 8 | MicroStation | Bentley Systems | Offers robust modeling and drafting capabilities |
| 9 | Chief Architect | Chief Architect, Inc. | Specialized in residential and light commercial design |
| 10 | Vectorworks Architect | Vectorworks, Inc. | Known for its flexibility and design capabilities |
| 11 | Allplan | Nemetschek Group | A BIM solution for architects and engineers |
Detailed insights into each of the 11 architectural engineering software
As an expert in CAD software, I’ll provide detailed insights into each of the 11 architectural engineering software tools you’ve listed, focusing on their descriptions, characteristics, pros, cons, and their utility for architects.
AutoCAD
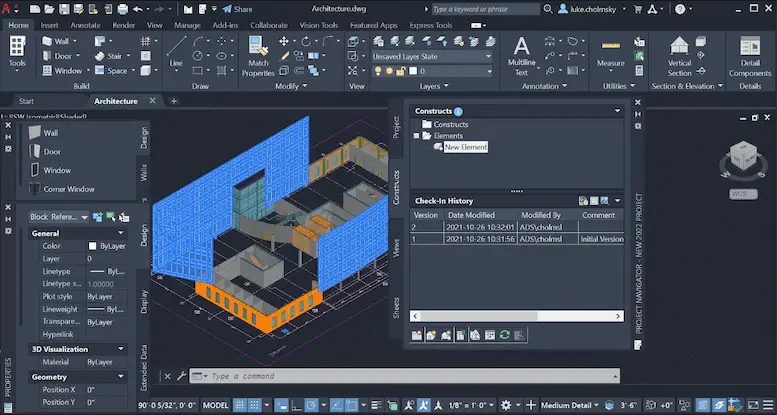
AutoCAD, a cornerstone in the world of 2D and 3D CAD design, is renowned for its versatile drafting tools and rich customization capabilities. This software has become a fundamental element in the toolkit of architects, engineers, and designers.
Characteristics:
- Extensive Library: AutoCAD boasts a comprehensive collection of standard shapes and tools, making it a go-to for various drafting needs.
- Layer Management: It offers sophisticated layer management, allowing for efficient organization and easy manipulation of complex drawings.
- Industry-Specific Features: The software comes equipped with specialized toolsets tailored for architecture, mechanical engineering, electrical design, and more.
Pros:
- High Precision: Its ability to deliver extremely accurate designs is unparalleled, making it indispensable for technical drawings.
- Customizable Interface: Users can tailor the workspace to their needs, enhancing productivity and ease of use.
- Wide Industry Acceptance: AutoCAD’s widespread adoption across industries ensures compatibility and standardization in design practices.
Cons:
- Complex for Beginners: The vast array of features can be overwhelming for novices, requiring a significant investment in learning.
- Relatively Expensive: Its comprehensive functionality comes at a cost, making it a heavier investment compared to some alternatives.
Usage in Architecture:
- Detailed Drafting: AutoCAD excels in creating detailed architectural drafts, a must-have for any construction project.
- Precise Floor Plans: Architects rely on it for developing highly precise and detailed floor plans, crucial in the initial phases of design.
- Complex Design Renderings: It enables the creation of complex and detailed renderings, helping architects visualize and present their ideas effectively.
Revit
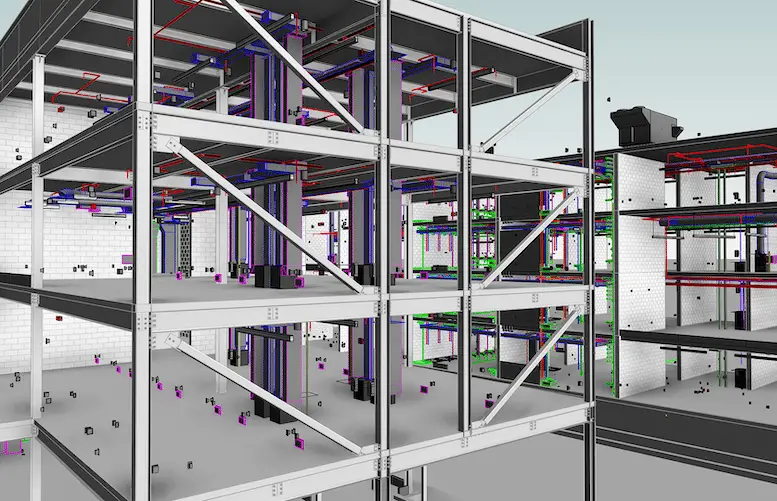
Revit stands as a powerhouse in the field of BIM (Building Information Modeling), tailor-made for collaborative and multidisciplinary projects. It’s a go-to solution for architects, engineers, and construction professionals seeking a unified approach to building design and construction.
Characteristics:
- Parametric Modeling Capabilities: Revit excels in parametric modeling, allowing users to create intelligent building components that automatically adjust and adapt to design changes.
- Real-time Collaboration Tools: It facilitates seamless collaboration among team members, crucial for large-scale and complex projects.
- Integrated Project Delivery (IPD): Revit supports IPD, integrating people, systems, business structures, and practices into a process that collaboratively harnesses the talents and insights of all participants.
Pros:
- Excellence in BIM: Its capabilities in BIM are top-notch, making it a standard in the industry for building modeling.
- Efficient Project Coordination: Revit greatly enhances coordination and communication among different disciplines, streamlining the design process.
- Error Reduction: By enabling a more integrated and informed approach to design and construction, Revit helps in significantly reducing errors and omissions in project documentation.
Cons:
- Steep Learning Curve: For newcomers, Revit can be challenging to master, requiring dedicated time and effort to become proficient.
- Resource-Intensive: It demands considerable computing power, especially for larger projects, which might be a constraint for some users or firms.
Usage in Architecture:
- Comprehensive Building Modeling: From conceptual design to detailed construction documentation, Revit provides architects with the tools to create detailed and coordinated building models.
- Concept to Construction: It’s extensively used by architects to manage the entire building design and construction lifecycle, from the initial concept to the final construction stages.
SketchUp

SketchUp is celebrated for its user-friendly interface, making it a preferred choice for quick and efficient 3D modeling. It’s particularly popular among architects, designers, and hobbyists who value simplicity and speed in their design process.
Characteristics:
- Intuitive Drag-and-Drop Interface: SketchUp’s interface is designed for ease of use, allowing even beginners to create 3D models with minimal training.
- Extensive Plugin Library: The software is supported by a vast array of plugins, enhancing its functionality and versatility.
- Real-Time Visualization: It offers immediate visual feedback, enabling designers to see changes as they happen, which is crucial for iterative design processes.
Pros:
- Easy to Learn: SketchUp is known for its low learning curve, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
- Flexible: The software is highly adaptable to various design needs, from interior design to landscape architecture.
- Vibrant User Community: SketchUp has a strong and active community, offering a wealth of resources, tutorials, and shared models.
Cons:
- Less Suitable for Complex Modeling: While excellent for basic and medium complexity models, it may fall short for more complex or intricate designs.
- Not Ideal for Large-Scale Projects: SketchUp can struggle with very large or detailed architectural projects, where more advanced BIM or CAD software might be preferable.
Usage in Architecture:
- Early-Stage Design: Architects often turn to SketchUp for initial concept development, where speed and flexibility are key.
- Conceptual Modeling: It’s an excellent tool for quickly modeling design ideas and exploring alternatives.
- Client Presentations: With its ability to produce clear and visually appealing models, SketchUp is frequently used for presenting ideas to clients.
ArchiCAD

ArchiCAD stands out as a BIM-focused software, highly regarded for its integrated design approach and collaborative workflows. It is a key tool for architects and designers looking to leverage the advantages of Building Information Modeling in their projects.
Characteristics:
- Strong BIM Capabilities: ArchiCAD is equipped with robust BIM functionality, enabling the creation of detailed and intelligent building models.
- Energy Analysis: The software includes advanced features for conducting energy and environmental analysis, vital for modern sustainable design.
- Customizable Object Creation: Users can craft custom objects and elements specific to their project needs, enhancing design flexibility.
Pros:
- Good Interoperability: ArchiCAD offers excellent compatibility with various other design and analysis tools, facilitating a seamless workflow across different software.
- User-Friendly: Despite its comprehensive capabilities, ArchiCAD is known for a relatively user-friendly interface, easing the learning curve.
- Great for Sustainable Design: With built-in tools for environmental analysis, it’s a preferred choice for projects focusing on sustainability and energy efficiency.
Cons:
- Can Be Costly: The extensive range of features and capabilities comes at a price, making ArchiCAD a significant investment.
- Interface Less Intuitive than Competitors: Some users might find its interface less intuitive compared to other BIM software like Revit, potentially impacting workflow efficiency.
Usage in Architecture:
- Complex Architectural Projects: ArchiCAD is often used in creating detailed architectural designs, particularly beneficial in complex and large-scale projects.
- Urban Planning: Its capabilities extend to the broader scope of urban and spatial planning, aiding architects in large-scale development planning.
- Interior Design: The software is also well-suited for detailed interior design work, providing tools for both aesthetic and functional aspects of interior spaces.
Rhino 3D
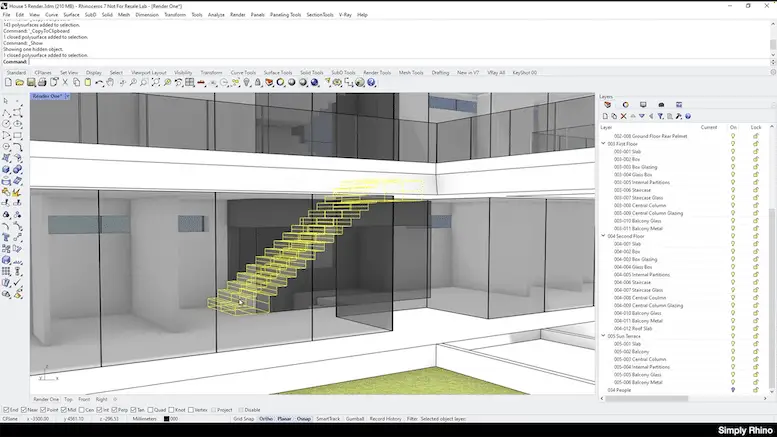
Rhino 3D is celebrated in the realm of CAD for its prowess in handling complex geometries and free-form 3D modeling. This software is a top choice for architects and designers who deal with intricate shapes and non-standard forms.
Characteristics:
- NURBS Modeling: Rhino excels at NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) modeling, allowing the creation of mathematically precise curves and surfaces.
- High-Quality Rendering: The software is capable of producing exceptionally high-quality renderings, crucial for visualizing designs before they are built.
- Scripting in Grasshopper: Rhino is integrated with Grasshopper, a visual programming language tool that enables highly customizable and complex design automation.
Pros:
- Exceptional for Complex Shapes: It stands out in its ability to model very complex and intricate shapes that are difficult to achieve in other CAD software.
- High Compatibility with Other Software: Rhino is known for its excellent compatibility, making it easy to integrate into various design workflows.
- Extensive Modeling Tools: The software provides a broad range of modeling tools, giving designers the flexibility to express their creativity without constraints.
Cons:
- Overwhelming for Beginners: The vast capabilities and the interface can be quite daunting for those new to 3D modeling.
- Less Focused on BIM: Unlike software like Revit or ArchiCAD, Rhino is less centered on BIM, focusing more on free-form modeling.
Usage in Architecture:
- Advanced Architectural Forms: Rhino is often the go-to software for designing complex architectural forms and structures that require a high level of geometric precision.
- Façade Design: It’s particularly useful in creating detailed and innovative façade designs, a critical aspect of modern architecture.
- Integrative Design Processes: Architects utilize Rhino in integrative design processes, often in conjunction with other software, for both conceptual and detailed design development.
3ds Max

3ds Max stands as a pillar in the CAD and 3D modeling world, distinguished for its robust 3D modeling, animation, and rendering capabilities. This software is a preferred choice for professionals in architecture, game development, and film who demand high-end visualizations and animations.
Characteristics:
- Advanced Polygon and Texture Modeling: 3ds Max offers sophisticated tools for polygon modeling and texturing, allowing for the creation of intricate and realistic models.
- High-End Rendering: It includes powerful rendering engines like Arnold, enabling the production of stunningly realistic imagery.
- Animation Tools: The software provides an extensive set of tools for animation, making it possible to bring models to life with realistic movements and behaviors.
Pros:
- Excellent for Visualization and Animations: 3ds Max excels in creating high-quality visualizations and animations, making it a top choice for presentations and marketing materials.
- Realistic Renderings: Its rendering capabilities are renowned for producing extremely realistic and detailed images.
- Detailed Models: The software’s tools allow for the creation of highly detailed and complex models, essential in architectural visualization.
Cons:
- Significant Training Required: To fully leverage 3ds Max’s capabilities, a considerable amount of learning and practice is necessary, especially for those new to 3D modeling.
- Resource-Heavy: It demands high computing power, particularly for rendering complex scenes or large-scale projects.
Usage in Architecture:
- Detailed Architectural Visualizations: Architects use 3ds Max for creating detailed and realistic visualizations of their designs, essential for client presentations and design approvals.
- Walkthroughs: The software is ideal for producing architectural walkthroughs, offering viewers a virtual tour of a proposed space.
- Animated Presentations: 3ds Max enables architects to create engaging animated presentations, helping in effectively communicating design concepts and ideas.
Civil 3D
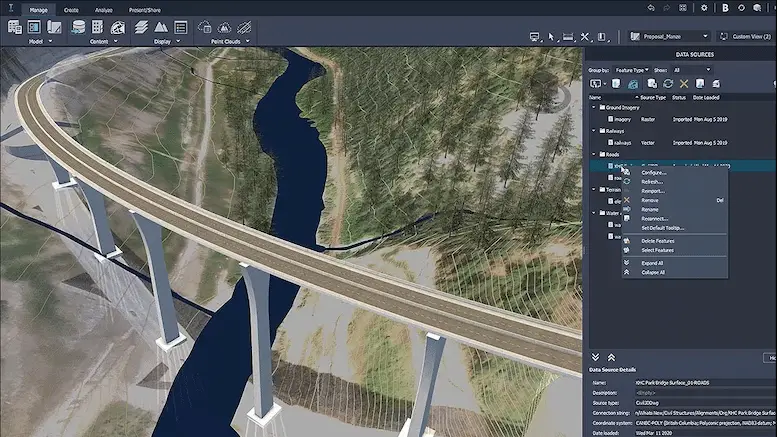
Civil 3D, a cornerstone in the civil engineering and land development software landscape, is engineered to enhance design and documentation workflows. It’s recognized for its robust support in BIM (Building Information Modeling) workflows, catering specifically to civil engineering projects.
Characteristics:
- Dynamic Design Functionality: The software provides tools for dynamic modeling, meaning design changes are automatically updated across project elements.
- Geospatial Analysis: Civil 3D includes advanced geospatial analysis tools for handling topography and terrain data, crucial in large-scale land development.
- Integrated Collaboration Tools: It promotes team collaboration with tools that support data sharing and project management, ensuring all stakeholders are in sync.
Pros:
- Ideal for Infrastructure Projects: Civil 3D is tailored for infrastructure project planning, from roads to water systems.
- Dynamic Updates: Its dynamic update feature ensures that any change made in the design is reflected throughout the project, reducing errors and saving time.
- Comprehensive Design Capabilities: The software offers a broad set of design tools that cover everything from simple grading to complex transportation design.
Cons:
- Learning Curve: Civil 3D is a specialized tool that requires time and training to master, particularly for those new to civil engineering software.
- Primarily for Civil Engineering: Its focus is mainly on civil engineering, making it less suitable for general architectural design purposes.
Usage in Civil Engineering and Urban Planning:
- Urban Planning: Civil 3D supports urban planners in creating sustainable and well-planned urban spaces.
- Land Development: The software is widely used in land development projects, including site planning, environmental impact studies, and utility layout.
- Infrastructure Design: It’s a go-to tool for designing transportation, drainage, sewer, and other infrastructure systems, essential in modern civil engineering.
MicroStation
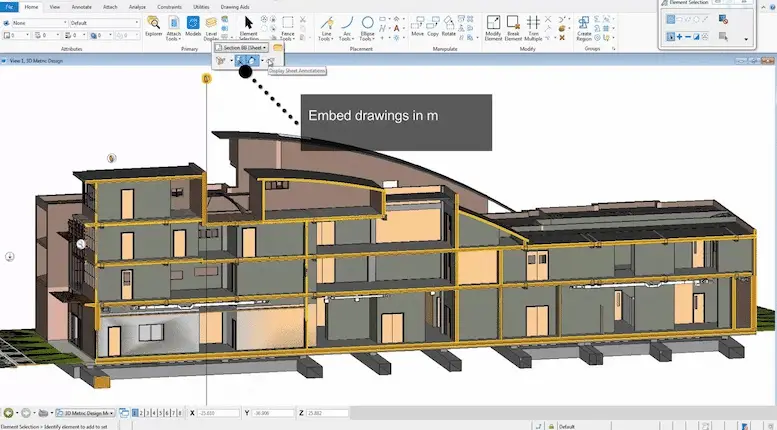
MicroStation is a high-end CAD software known for its robust modeling and drafting capabilities. It’s a powerful tool widely used in the fields of architecture, engineering, and construction for creating detailed and precise designs, especially in large-scale projects.
Characteristics:
- Stability: The software is recognized for its reliable performance, crucial when working on complex and data-intensive projects.
- High-Quality Visuals: MicroStation enables the creation of highly detailed and realistic visualizations, elevating the presentation of design projects.
- Flexible Modeling Tools: It offers a wide range of modeling tools that cater to various design needs, from simple 2D drawings to complex 3D models.
Pros:
- Ideal for Large-Scale Projects: The software’s powerful capabilities make it particularly suitable for handling large and complex projects, such as infrastructure and urban development.
- High Precision: MicroStation is known for its exceptional precision and accuracy in design, which is essential in professional CAD work.
- Good Interoperability: It works well with other software and data formats, making it a versatile choice in multi-software workflows.
Cons:
- More Expensive: Compared to some other CAD software like AutoCAD, MicroStation can be more costly, which might be a consideration for smaller firms or individual professionals.
- Less Popular Than AutoCAD: Its lesser popularity compared to AutoCAD means there are fewer community resources and a smaller user base.
Usage in Design and Mapping:
- Complex Architectural Projects: Architects and designers use MicroStation for creating detailed architectural plans and models, particularly in large and complex buildings.
- Infrastructure Projects: It’s widely employed in designing major infrastructure projects like bridges, roads, and transit systems.
- Geospatial Mapping: MicroStation also finds its use in geospatial mapping, providing tools for integrating CAD designs with geographic information systems (GIS).
Chief Architect

Chief Architect is a CAD software specialized in residential and light commercial design. It’s highly regarded for its advanced building tools and the ability to produce realistic renderings, making it a favorite among home builders, remodelers, and interior designers.
Characteristics:
- Automated Building Tools: The software offers automated tools for creating a variety of building elements such as walls, roofs, and stairs, significantly speeding up the design process.
- 3D Modeling: Chief Architect provides robust 3D modeling capabilities, allowing designers to visualize spaces in three dimensions effectively.
- Large Libraries of Objects: It includes extensive libraries of pre-designed objects, from furniture to fixtures, which can be easily incorporated into designs.
Pros:
- User-Friendly: The software is intuitive and easy to navigate, even for those new to CAD software, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
- Excellent for Home Design: Chief Architect excels in residential design, offering specialized tools and features for home planning and remodeling.
- Quick Conceptual Sketches: It is adept at creating fast and effective conceptual sketches, a key aspect in the initial stages of residential design.
Cons:
- Less Versatile for Non-Residential Projects: While outstanding in residential design, it’s less equipped for commercial or industrial projects.
- Limited for Large-Scale Urban Design: Chief Architect may not be the best fit for large-scale urban planning or complex architectural projects due to its focus on residential design.
Usage:
- Ideal for Home Builders and Remodelers: The software is widely used by professionals in home building and remodeling, thanks to its specialized toolset and user-friendly approach.
- Interior Design: Interior designers find Chief Architect beneficial for creating detailed interior layouts, including furniture arrangements and color schemes.
Vectorworks Architect
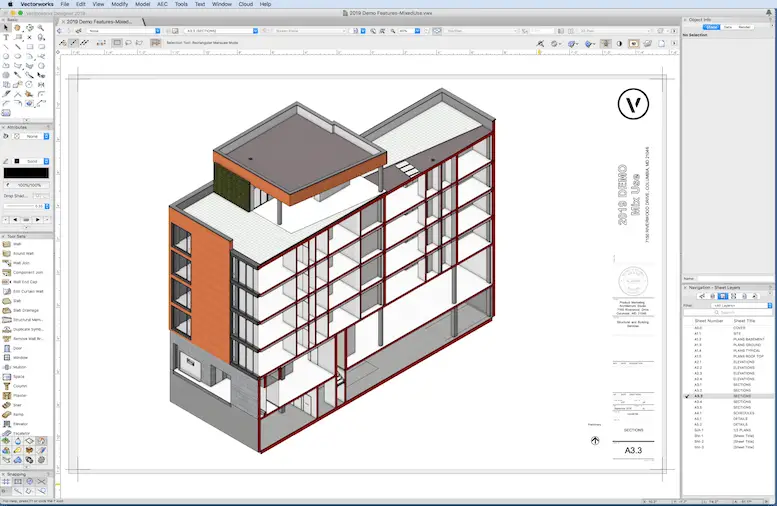
Vectorworks Architect is recognized for its flexibility and comprehensive design capabilities, making it a versatile choice in the world of design and BIM (Building Information Modeling) software. It caters to a wide spectrum of design needs, from architectural and landscape design to urban planning.
Characteristics:
- 2D Drawing and 3D Modeling: The software seamlessly integrates 2D drawing and 3D modeling capabilities, allowing designers to transition smoothly between different stages of design.
- Fully Integrated BIM: Vectorworks Architect offers a fully integrated BIM solution, enabling architects to create detailed, data-rich models that are vital for modern building design.
- Comprehensive Design Tools: The toolset includes everything from basic drafting to advanced modeling and visualization features, supporting a wide range of design processes.
Pros:
- Versatility: Its broad range of functions makes it suitable for various types of design work, from small residential projects to large-scale urban developments.
- Good for Collaboration: The software’s compatibility with other tools and formats makes it ideal for collaborative projects, facilitating seamless teamwork and data sharing.
- Strong Rendering Capabilities: Vectorworks Architect is equipped with powerful rendering tools, allowing for the creation of visually impressive and realistic representations of designs.
Cons:
- Additional Training May Be Required: To fully utilize its extensive capabilities, users might need additional training, especially those who are new to BIM software.
- Interface Less Intuitive for Some: While powerful, some users find its interface less intuitive compared to other CAD and BIM software, which could affect workflow efficiency.
Usage in Design and Planning:
- Architectural Design: The software is widely used in creating detailed architectural designs, from initial concepts to construction documents.
- Landscape Design: Its tools are also well-suited for landscape design, allowing for the integration of architectural and environmental elements.
- Urban Planning: Vectorworks Architect supports urban planning projects, offering tools for large-scale planning and analysis.
Allplan
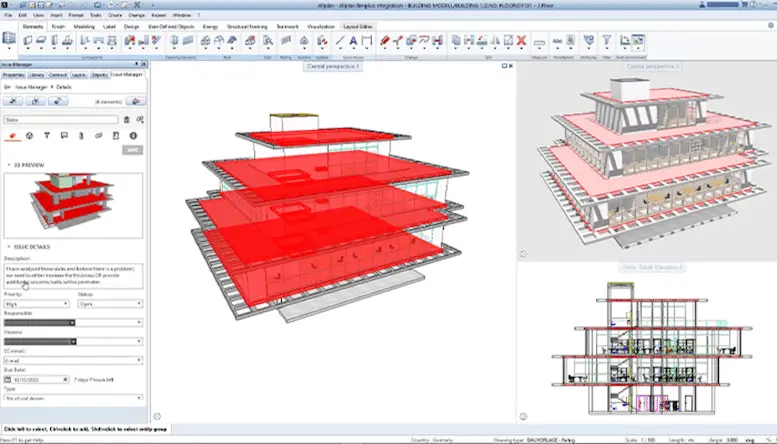
Allplan is a specialized BIM (Building Information Modeling) solution designed for architects and engineers. It emphasizes efficiency and accuracy in the planning, design, and execution of construction projects. This software is particularly known for its detailed approach to BIM, making it a valuable tool in complex architectural and engineering endeavors.
Characteristics:
- Detailed BIM Planning Tools: Allplan provides a comprehensive suite of BIM tools, enabling users to create detailed and data-rich models.
- High-Quality Visuals: The software excels in producing high-quality visualizations, enhancing the understanding and presentation of projects.
- Data Management: Allplan offers robust data management capabilities, crucial for handling the vast amount of information typically involved in construction projects.
Pros:
- Excellent for Detailed Design and Construction Planning: It’s highly effective in creating detailed designs and facilitating thorough construction planning.
- Strong BIM Capabilities: Allplan’s BIM functionalities are among the best in the industry, catering to the complex needs of modern architectural and engineering projects.
Cons:
- Less Known in the Market: While powerful, Allplan is not as widely recognized as some other BIM software like Revit, which might impact its adoption and collaboration potential.
- Learning Curve: The software’s comprehensive features can present a learning curve, particularly for those not familiar with advanced BIM tools.
Usage:
- Complex Architectural and Engineering Projects: Allplan is particularly well-suited for handling complex and large-scale architectural and engineering projects, where detail and precision are paramount.
- Popular in Europe: It has a strong presence in the European market, where it’s often used for significant construction and infrastructure projects.
This article “Top 11 Architectural Engineering Software” provides an overview of key software tools used in the architectural engineering field. Each software has unique features catering to various aspects of architectural design and engineering.
- AutoCAD: A staple for 2D and 3D CAD design, known for its precision and customizable interface, but complex for beginners.
- Revit: A BIM-focused tool ideal for collaborative projects, offering real-time collaboration and integrated project delivery, though it has a steep learning curve.
- SketchUp: Renowned for its user-friendly interface, it is great for quick 3D modeling but less suitable for complex modeling.
- ArchiCAD: Offers strong BIM capabilities and energy analysis, useful for complex projects, with good interoperability but at a higher cost.
- Rhino 3D: Known for handling complex geometries and free-form 3D modeling, it has extensive modeling tools but can be overwhelming for beginners.
- 3ds Max: A top choice for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering, suitable for detailed visualizations but requires significant training.
- Civil 3D: Specialized in civil engineering design, supports BIM workflows, ideal for infrastructure projects but primarily focuses on civil engineering.
- MicroStation: Offers robust modeling and drafting capabilities, excellent for large-scale projects, but can be expensive and less popular than other software.
- Chief Architect: Specialized in residential and light commercial design, known for its building tools and realistic renderings, but less versatile for non-residential projects.
- Vectorworks Architect: Known for its flexibility and strong rendering capabilities, it’s versatile but may require additional training for new users.
- Allplan: A BIM solution focusing on efficiency and accuracy, great for detailed design and construction planning, but less known in the market.
Each software in this list has been chosen for its specific strengths and capabilities, addressing different needs and aspects of architectural engineering, from initial design to detailed construction planning.

